Foundation(6)
Webhacking 강좌는 여러 절로 구성되어 있습니다.
- Foundation
- Foundation(1)
- Foundation(2)
- Foundation(3)
- Foundation(4)
- Foundation(5)
- Foundation(6)
- Foundation(7)
- Foundation(8)
- Assemble
PHP , MYSQL , JS , CSS+HTML 순으로 진행하겠습니다.
PHP
PHP 함수의 형식
함수(function)
프로그램에서 반복적으로 사용할 수 있는 문자의 블록을 의미한다.
형식
function 함수이름(매개변수1, 매개변수2,…)
{
함수가 호출되었을 때 실행될 코드;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Function</h1>
<h2>Basic</h2>
<?php
function basic(){ // function을 사용자 정의 함수를 만든다.
print("PHP function useful!<br>");
print("PHP function useful!!<br>");
}
basic(); // 'PHP function useful!<br>PHP function useful!!<br>' 출력
basic(); // 'PHP function useful!<br>PHP function useful!!<br>' 출력
?>
<h2>parameter & argument</h2> <!-- parameter :: 함수 등에서 사용되는 전달된 값을 받는 변수
argument :: 값, 변수, 참조 등 전달되는 값 -->
<?php
function sum($left, $right){ // 함수 안에 parameter를 사용해서 argument를 받을 수 있도록 설정한다.
print($left+$right);
print("<br>");
}
sum(2,4); // '6' 출력
sum(4,6); // '10' 출력
?>
<h2>return</h2> <!-- 위에 sum()함수는 값을 더하고 출력하는 것이 고정이기에, 범용성이 작다.-->
<?php
function sum2($left, $right){ // 그러나 sum2() 는 값을 리턴해주기 때문에, 범용성이 넓다.
return $left + $right; // 함수에서 return이 나오면 함수가 종료된다.
}
print(sum2(2,4)); // '6' 출력
file_put_contents('result.txt', sum2(2,4)); // result.txt라는 파일을 생성하고, 안에 '6'을 입력
// email('example@exapme.com', sum2(2,4));
// upload('example.com', sum2(2,4));
?>
</body>
</html>
++ 함수의 활용
index.php에서 함수를 이용하면 본문 코드 내용을 보기 간편하고, 중복되는 코드의 양을 줄일 수 있다.
원본 코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>
<?php
if(isset($_GET["id"])) { // 7 ~ 13 라인과 43 ~ 49 라인이 중복된 것을 확인
echo $_GET["id"];
} else {
echo "Welcome!";
}
?>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.php">WEB</a></h1>
<ol>
<?php
$list = scandir('./data');
$i = 0;
while($i < count($list)) {
if($list[$i] != '.' && $list[$i] != '..') {
echo "<li><a href=\"index.php?id=$list[$i]\">$list[$i]</a></li>\n";
}
$i += 1;
}
?>
</ol>
<h2>
<?php
if(isset($_GET["id"])) {
echo $_GET["id"];
} else {
echo "Welcome!";
}
?>
</h2>
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id'])) {
echo file_get_contents("data/".$_GET['id']);
} else {
echo "This is 'index.php' file";
?>
</body>
</html>
중복된 부분을 함수로 정의하여 정리한 코드
<?php
function print_title(){
if(isset($_GET["id"])) {
echo $_GET["id"];
} else {
echo "Welcome!";
}
}
function print_description(){
if(isset($_GET['id'])) {
echo file_get_contents("data/".$_GET['id']);
} else {
echo "This is 'index.php' file";
}
}
function print_list(){
$list = scandir('./data');
$i = 0;
while($i < count($list)) {
if($list[$i] != '.' && $list[$i] != '..') {
echo "<li><a href=\"index.php?id=$list[$i]\">$list[$i]</a></li>\n";
}
$i += 1;
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>
<?php
print_title();
?>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.php">WEB</a></h1>
<ol>
<?php
print_list();
?>
</ol>
<h2>
<?php
print_title();
?>
</h2>
<?php
print_description();
?>
</body>
</html>
MySQL
MySQL 관계형 DB
관계형 DB는 데이터 항목 간에 사전 정의된 관계가 있을 때, 그러한 데이터 항목들의 모음을 의미한다.
관계형 DB의 필요성
데이터가 중복된다라는 의미는 퍼포먼스와 유지보수의 측면에서 개선의 여지가 있다는 강력한 증거이므로, 이떄 관계형 DB를 사용하면 별도의 참조 테이블을 만들어 쉽게 관리할 수 있다.
기존의 테이블 >
중복되는 데이터를 분리한 테이블 >
MySQL 테이블 분리하기
- ‘author’ 테이블과 ‘topic’ 테이블을 만든다.
CREATE TABLE `author` (-> `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> `name` varchar(20) NOT NULL, -> `profile` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, -> PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ========================================== mysql> CREATE TABLE topic( -> id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> title VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, -> description TEXT NULL, -> created DATETIME NOT NULL, -> author_id INT(11) NULL, -> PRIMARY KEY(id) -> );
2. 각각의 테이블안에 데이터를 입력한다.
> ```MySQL
><author TABLE>
INSERT INTO `author` VALUES (1,'joho','developer');
INSERT INTO `author` VALUES (2,'joy','Artist');
INSERT INTO `author` VALUES (3,'daisy', 'Artist, developer');
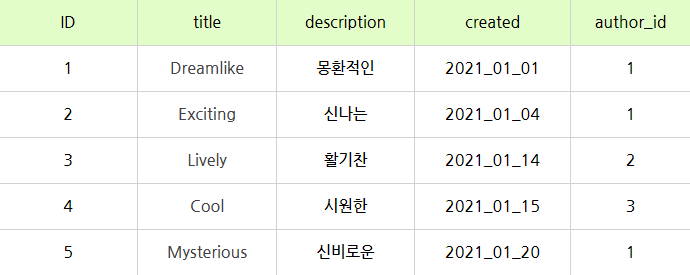
<topic TABLE> INSERT INTO topic (id, title, description, created, author_id) VALUES (1,'Dreamlike','몽환적인','2021_01_01',1); INSERT INTO topic (id, title, description, created, author_id) VALUES (2,'Exciting','신나는','2021_01_04',1); INSERT INTO topic (id, title, description, created, author_id) VALUES (3,'Lively','활기찬','2021_01_14',2); INSERT INTO topic (id, title, description, created, author_id) VALUES (4,'Cool','시원한','2021_01_15',3); INSERT INTO topic (id, title, description, created, author_id) VALUES (5,'Mysterious','신비로운','2021_01_20',1);
MySQL JOIN
여러 테이블에 흩어져 있는 정보 중 사용자가 필요한 정보만 가져와서 가상의 테이블 처럼 만들어서 결과를 보여주는 것으로 2개의 테이블을 조합하여 하나의 열로 표현하는 것을 의미한다.
mysql> SELECT * FROM topic LEFT JOIN author ON topic.author_id = author.id;
JavaScript
JS 배열
배열(Array)
한번에 하나 이상의 값들을 담을 수 있는 특별한 변수이다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Array</h1>
<h2>Syntax</h2>
<script>
var coworkers = ["egoing", "leezche"];
</script>
<h2>get</h2>
<script>
document.write(coworkers[0]); // 'egoing' 출력
document.write(coworkers[1]); // 'leezche' 출력
</script>
<h2>add</h2>
<script>
coworkers.push("duru"); // 배열에 데이터를 추가
coworkers.push("taeho");
</script>
<h2>count</h2>
<script>
document.write(coworkers.length); // 배열의 길이를 출력 :: '4' 출력
</script>
</body>
</html>
JS 반복문
반복문(loop)
반복문은 조건식이 참일때까지 반복적으로 작업을 진행한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>loop</h1>
<ul>
<script>
document.write("<li>1</li>");
var i = 0;
while (i < 3) {
// i의 값이 3이 되었을 떄, 반복문 탈출
document.write("<li>2</li>"); // *2 *3 (총 3번 반복 출력)
document.write("<li>3</li>");
i += 1;
}
document.write("<li>4</li>");
</script>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
JS 배열과 반복문
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Loop & Array</h1>
<script>
var coworkers = ["egoing", "leezche", "duru", "taeho"]; // 배열 생성
</script>
<h2>Co workers</h2>
<ul>
<script>
var i = 0;
while (i < coworkers.length) {
// 배열의 길이를 받아와서 반복 횟수를 정한다.
document.write("<li>" + coworkers[i] + "</li>");
i += 1; // i의 값을 증가시켜서 반복문을 빠져나오게 한다.
}
</script>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
<결과>
++ 배열과 반복문 활용
ex3.html 파일을 활용하여 링크의 색을 바꾸려고 한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.html">WEB</a></h1>
<input
id="night_day"
type="button"
value="night"
onclick="
var target = document.querySelector('body');
if(this.value === 'night'){
target.style.backgroundColor = 'black';
target.style.color = 'white';
this.value = 'day';
var alist = document.querySelectorAll('a'); // 'a' 태그가 포합된 모든 코드를 배열에 저장
var i = 0;
while(i < alist.length){ // alist 안에 배열의 길이를 가져와서 반복 횟수를 정함
console.log(alist[i]);
alist[i].style.color = 'powderblue'; // 각 태그에 색을 지정
i = i + 1;
}
} else {
target.style.backgroundColor = 'white';
target.style.color = 'black';
this.value = 'night';
var alist = document.querySelectorAll('a');
var i = 0;
while(i < alist.length){
console.log(alist[i]);
alist[i].style.color = 'blue';
i = i + 1;
}
}
"
/>
<ol>
<li><a href="1.html">HTML</a></li>
<li><a href="2.html">CSS</a></li>
<li><a href="3.html">JavaScript</a></li>
</ol>
<h2>JavaScript</h2>
<p>
JavaScript (/ˈdʒɑːvəˌskrɪpt/[6]), often abbreviated as JS, is a
high-level, dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based, multi-paradigm, and
interpreted programming language. Alongside HTML and CSS, JavaScript is
one of the three core technologies of World Wide Web content production.
It is used to make webpages interactive and provide online programs,
including video games. The majority of websites employ it, and all modern
web browsers support it without the need for plug-ins by means of a
built-in JavaScript engine. Each of the many JavaScript engines represent
a different implementation of JavaScript, all based on the ECMAScript
specification, with some engines not supporting the spec fully, and with
many engines supporting additional features beyond ECMA.
</p>
</body>
</html>
<결과>